Our universe is a hard concept to wrap our heads around, with its infinite density and never-ending phenomena that are just as scary as they sound.
In the past couple of days, you might’ve noticed more natural light that shimmers in the sky, reminding us all that we are a speck of dust in the vastness of the universe.
It all comes down to our Sun’s recent activities.
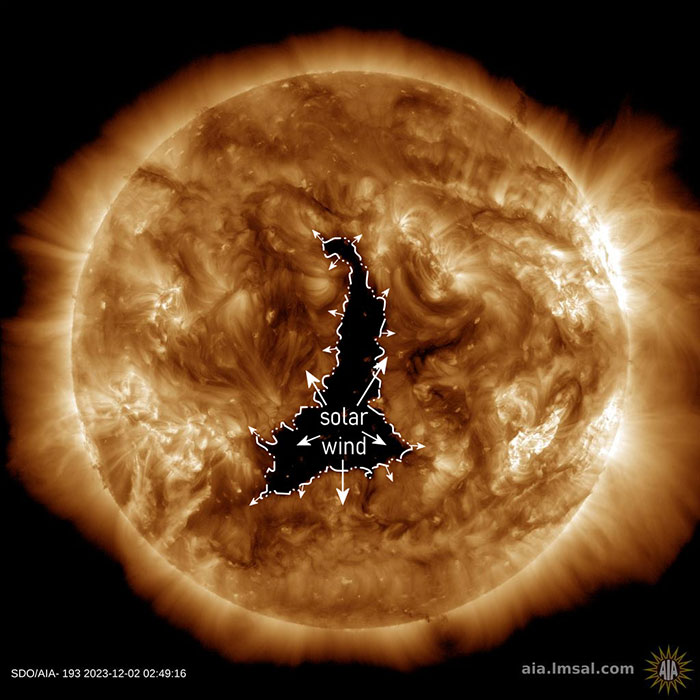
In latest cosmic news, scientists have reported that a colossal hole in the atmosphere of the Sun, more than five times larger than the diameter of Jupiter, is releasing a forceful solar wind that’s blasting through the Solar System.
A huge hole in the atmosphere of the Sun is releasing a forceful solar wind that’s blasting through the Solar System
Image credits: NASA/SDO
The hole in question has been identified as a coronal hole, a temporary region of relatively cool, less dense plasma in the solar corona that occurs when the magnetic fields that hold the sun in place suddenly open up.
The hole is currently rotating away from Earth – but a few days ago, from its position straddling the equator, it was pointed right at us, directing a stream of particles in Earth’s direction, Science Alert reported.
According to the publication, the result was nothing to be alarmed about – a mild solar storm – but the hole does reportedly contribute to a wider pattern of rampant solar shenanigans as we enter solar maximum.
A coronal hole is a temporary region of relatively cool plasma in the solar corona that occurs when the magnetic fields that hold the sun in place suddenly open up
Image credits: spaceweather
Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun’s 11-year solar cycle.
Reports suggest that the Sun has been rather disorderly in recent times, as it has been expected.
In order to arrive at the solar maximum, our star initially goes through activity cycles, in which it gets more active with sunspots, solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and coronal holes.
The hole is currently rotating away from Earth – but a few days ago, from its position straddling the equator, it was pointed right at us
Image credits: NASA/SDO
Solar maximum, which is when the sun’s activity escalates to a peak, occurs just before subsiding again towards solar minimum, a period of relative calm and minimal activity.
According to Science Alert, this cycle appears to be driven by, or coincides with, the Sun’s magnetic cycles, during which the solar magnetic field reverses polarity, and its north and south poles switch places.
Subsequently, this switch happens at solar maximum, which is due to take place sometime in 2024.
The hole contributes to a wider pattern of rampant solar shenanigans as we enter solar maximum
Image credits: NASA/SDO
Solar flares and coronal mass ejections are eruptions, often affiliated with sunspots, that are provoked by a significant amount of release of energy that occurs due to magnetic field lines snapping and reconnecting.
Unlike sunspots, coronal holes can’t be seen in optical light; however, when we look in ultraviolet wavelengths, we see huge, dark patches that are dimmer than their surroundings because they are cooler, the website stated.
Because the magnetic field is open, the wind that constantly blows from the Sun can reportedly escape more readily. As per Science Alert, the result is a more powerful gusting of solar particles and plasma out into the Solar System, flowing around any planets that may be in their path.
You can see the fascinating phenomenon below:
The current hole reportedly almost rotated away to the far side of the Sun. According to Spaceweather, it measures around 800,000 kilometers (500,000 miles) along its longest axis. Jupiter’s diameter is around 140,000 kilometers; Earth’s is 12,742.
The hole was facing Earth around 2 December, and the solar wind reportedly smacked into us over the course of 4 and 5 December.
BBC has reported that experts believe the most recent coronal hole spotted could lead to what’s known as a geomagnetic storm, which can lead to radio blackouts and auroras, which are the natural appearance of colorful light in the sky.
Nevertheless, this storm hasn’t reportedly turned out to be as powerful as scientists thought it would be.
Science fans weren’t too worried by the news
The British broadcaster has stated that it’s not known exactly how long the hole will last for, but experts say they can stick around for longer than a single rotation of the Sun, which is 27 days.
The region where the newly discovered coronal hole exists is expected to rotate away from Earth soon.
 Share icon
Share icon Share icon
Share icon Share icon
Share icon